The 3 Questions Of Economics
In This Article
-
What Are the Three Economic Questions?
-
5 Types of Economical Systems
-
Market Economies and the Round Menstruation Diagram
-
What Is Left Out of the Circular Flow Diagram
What Are the Iii Economical Questions?
Society has to grapple with three principal questions in deciding how to organize the economy.
These questions are:
-
What should be produced?
-
How should it be produced?
-
For whom should it exist produced?
Each of these questions is motivated by the same underlying trouble. Resources in the economy are scarce. There is not enough time, money, or appurtenances and services to satisfy every want of every person, and so somehow, society must make up one's mind how to produce and allocate goods and services using their limited resources.
5 Types of Economic Systems
Throughout history and across countries, society has answered the three economic questions in distinct ways. An economical system (or economical guild) refers to a particular way societies organize their economy.
The master economic systems are:
-
Traditional economies
-
Command economies
-
Planned economies
-
Capitalist or market-based economies
-
Mixed economies
1. Traditional Economies
Humans lived in traditional (or primitive) economies throughout much of history. In a traditional economy, households produce most of what they consume. Division of labor and market exchanges are limited in traditional economies, meaning the extent to which households exchange goods and services with people outside of their household and community is limited. The standard of living in traditional economies is low compared to many other economic systems, considering of lower productivity and slower technological progress.
2. Command Economies
In a command economy, a central dominance controls the means of production and makes most production and allocation decisions. Industries in a command economic system are publicly owned, and private property is express. Democratic people's republic of korea is an example of a country with a command economy.
iii. Planned Economies
A planned economy is like a command economic system in that authorities such as a central government make decisions and exercise control over the production and distribution of goods and services. These authorities tin allocate resource and set prices at their discretion. Planned economies differ from command economies because firms and industries may be privately endemic. Private companies, notwithstanding, must operate according to the plans and regulations set along by the government. The former Soviet Union and Cuba are examples of planned economies.
4. Capitalist or Market-Based Economies
Nigh economies today are market-based economies. In a market place-based economic system, economic decisions are determined mainly by markets and left upwards to individual conclusion making past households and businesses. The fundamental features of a market-based economy are markets, private property, and firms. A market-based economic system is as well sometimes called a gratis market economy or a laissez-faire economy.
5. Mixed Economies
A mixed economic system is an economic system with elements of 2 or more well-established economical systems. If a state uses both markets and land planning to produce goods and services, it is a mixed economy. China, which was once a centrally planned economic system, is now a mixed economy. It is neither a pure planned economy or pure market economy.
Market Economies and the Circular Flow Diagram
What Is the Round Flow Diagram?
Round flow diagrams, such as the ane shown below, are used to model the production and allocation of goods and services in a market-based economy.
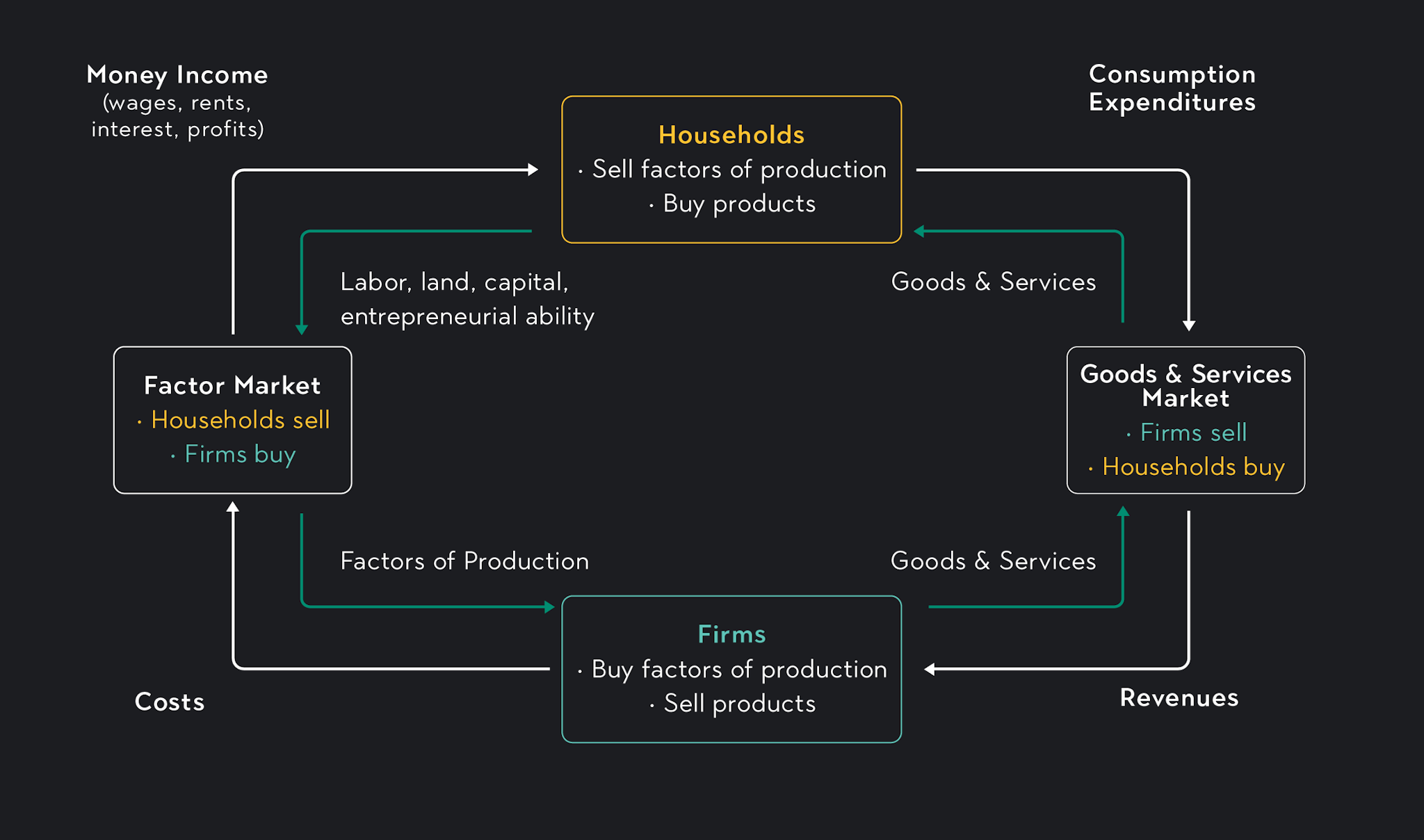
In a circular flow diagram, there are two main actors — firms and households. Firms and households interact in ii types of markets: markets for goods and services and markets for factors of production.
In the market for goods and services, firms sell their products to households. Households pay for these products using money they make in gene markets.
In factor markets, businesses buy or rent factors of product such as labor and majuscule from households. These factors are what firms use to produce their products. In exchange for the factors of product, households receive coin in the course of income.
Market-Based Economies and the Three Basic Economical Questions
Looking at the diagram, you can run into how market-based economies address the three basic economical questions.
What should be produced?
Firms decide what to produce based on consumer demand in a market-based economy. If firms can't sell their products to consumers in the goods and services market, firms won't earn acquirement and will not be able to stay in business.
How should information technology be produced?
Goods and services are produced through entrepreneurship and complimentary enterprise. Privately owned firms produce their goods using labor, capital, and other factors of production. Firms buy, rent, or rent these inputs from households in cistron markets.
For whom should information technology be produced?
Firms sell products to consumers who are willing to pay the cost set by the market. The interaction of supply and demand in the market determines the market toll.
What Is Left Out of the Circular Menstruum Diagram
Keep in listen that the circular menstruum diagram is a simplified model of marketplace-based economies. Market-based economies utilize markets as the principal way of producing and allocating appurtenances and services. Withal, economic activeness tin occur exterior of cistron markets and goods and services markets. For instance, household work, such as cleaning and child care, are economical activities that stay contained within the household. Such activities involve no market interactions.
Households might also exchange these services with other households. Firms might sell or purchase goods, services, and factors of product with other firms. And finally, the authorities plays a role in market-based economies by providing citizens with public goods and services such as national defence, public teaching, and healthcare. Rather than orchestrating the economic system as it would in a planned economy, the role of government in marketplace-based economies is to provide a safety net and to provide the goods and services that markets are not skillful at allocating. Government intervention is limited, but withal necessary in market economies.
The 3 Questions Of Economics,
Source: https://articles.outlier.org/the-three-economic-questions
Posted by: westbrookwhanderharty.blogspot.com


0 Response to "The 3 Questions Of Economics"
Post a Comment